The article, as the initial in the MESH series, introduces the architecture and functions of the Bluetooth mesh 1.0 protocol. As a supplementary protocol to the Bluetooth Low Energy protocol, the Bluetooth Mesh protocol, independent of Bluetooth 5.0, introduces an open standard mesh network to Bluetooth Low Energy devices for the first time.
MESH network is a low-power wireless technology for smart home and building automation applications. At first, because SIG lacks the support for MESH network, engineers have to change Bluetooth Low Energy to other technologies (such as ZigBee and Thread) for the development of the smart home applications. The situation lasted until the specification of Bluetooth mesh was made public in mid-2017. Now the Bluetooth SIG has solved the lack of MESH networking by introducing the Bluetooth 5.0 supplementary specification - Bluetooth mesh network 1.0. The specification does not need other hardware supports and can run on existing Bluetooth Low Energy chips (BLE4.0, BLE4.1, BLE4.2 and BLE5.0) by flashing the firmware. Some chip manufacturers can support the Bluetooth Mesh 1.0 protocol now.
1. BLE MESH Market Now
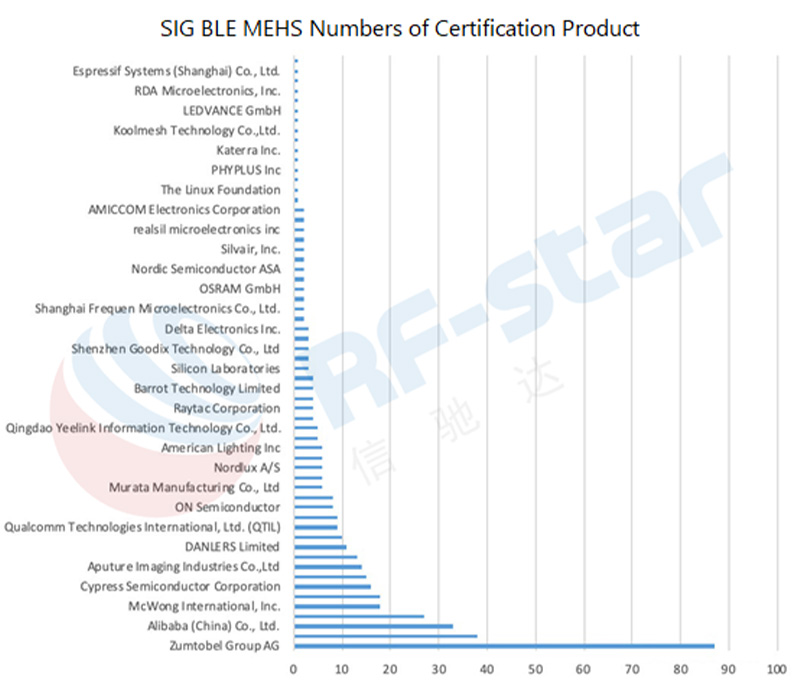
So far, 73 companies in the world have certified BLE MESH in the SIG, and the number of certified products is as high as 461. This data includes the total number of certifications of the terminal products and the chip. The following table lists the certified companies and the number of their product certifications, of which there are many terminal products certified by Chinese Internet giants.
2. Advantages of the MESH
Bluetooth Low Energy was originally designed to complement the high power consumption of "classic" Bluetooth by extending wireless technology to battery-powered devices. For example, the heart rate belts and wirelessly controlled toy applications communicate with a master device (such as a mobile phone) through Bluetooth Low Energy technology. Even a master device controls multiple slave devices to form a star network topology.
Due to the interoperability of Bluetooth low energy and mobile phones, Bluetooth low energy can be quickly extended to other applications such as lighting control, smart home, etc. In these types of applications, the shortcomings of the star network appear. For example, Bluetooth low energy solutions can only cope with a limited number of simultaneous connections (usually eight). And lighting devices with more than 8 bulbs cannot be controlled by a single command, which will cause control delays. The light bulbs far away from the big house may not be within the range of the central controller, and it need to be switched by nodes with routing functions.
Since the launch of Bluetooth Low Energy, it has launched versions 4.1, 4.2, 5.0, 5.1, and 5.2. Many functions in the protocol have been enhanced, such as transmission range, throughput, carrying capacity of broadcast data, AoA/AoD positioning, and coexistence improvements. (some of these new features are optional. Optional means that a chip that does not support these new functions can also be a BLE 5.0 chip).
Bluetooth Mesh 1.0 is not a simple upgrade of BLE 5, but a set of protocols independent of the Bluetooth protocol. And any previous version (BLE 4.0, BLE 4.1, BLE 4.2, BLE 5.0) chip products can be upgraded. Under the premise of sufficient Flash and RAM resources, it only needs to upgrade the firmware to run the Bluetooth mesh.
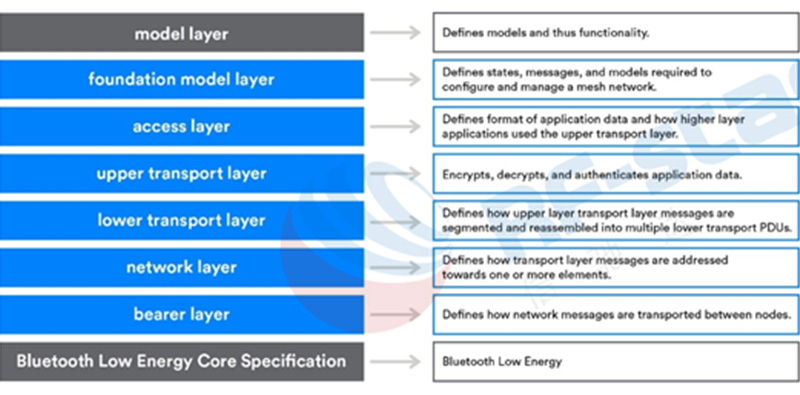
When the Bluetooth MESH node receives a message, it transfers the data obtained from the Bluetooth low energy layer to the bearer layer, then the data is transferred to the network layer through the bearer layer. The network layer uses various checks to decide whether to pass the message to the lower transport layer or discard it.
The Bluetooth MESH specification defines a new core protocol. Some of the core protocol layers share some concepts with the Bluetooth low energy core protocol layers, but the two protocols are not completely compatible with each other. This is different from technologies such as ZigBee and Thread. ZigBee and Thread have been designed as MESH networks from the beginning. The underlying specifications are based on 802.15.4, but the compatibility of other mainstream protocols has not been considered. (In the past two years, ZigBee has considered using dotdot at the top level to be compatible with other network protocols and achieve interconnection. For details, please refer to https://zigbeealliance.org/solution/dotdot/)
There are four types of network nodes:
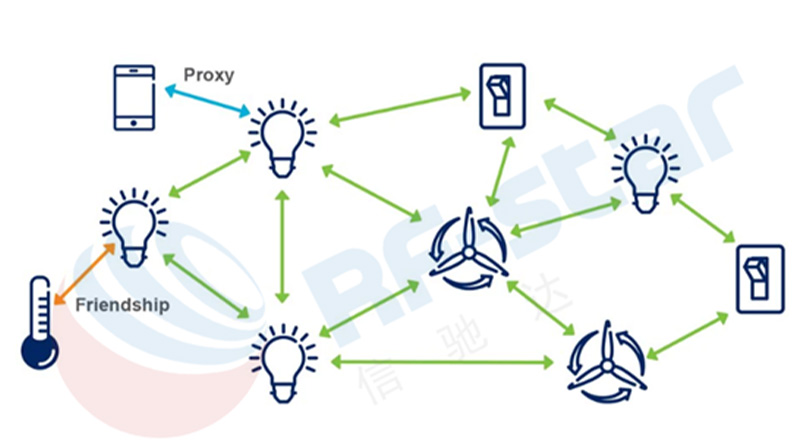
A Relay Node receives and retransmits Bluetooth mesh messages using the advertising bearer. The disadvantage of relay nodes is that they must always keep the alert state, which will greatly increase power consumption. It has little effect on applications powered by main power such as smart lighting, but it is a big problem for battery-powered nodes such as switches incorporated into the network.
Low power nodes use the standard power-saving features of Bluetooth Low Energy (that is keeping sleep state for a long time), so they can run for a long time through battery or energy harvesting. LPNs work in tandem with Friend node, one which is not power-constrained (e.g.it has a permanent AC power source). The Friend stores messages addressed to the LPN and delivers them to the LPN whenever the LPN polls the Friend node for “waiting messages”. When the LPN enters the receiving mode (according to a predetermined schedule), it receives the stored message and follows the instructions, then returns to the energy-saving sleep mode.
Friend Nodes
A Friend Node can store and later forward messages addressed to an associated Low Power Node. When a Low power node wakes up and polls a Friend node, Friend will transmit these messages to the relevant Low power node. Friend nodes will occupy more memory than other types of nodes because it needs to store messages for one or more Low power nodes. The required memory size depends on the amount of data /commands that need to be stored in Friend nodes and sent to Low power nodes during polling operations.
Proxy Nodes
The Proxy Node is the key to enabling non-mesh Bluetooth Low Energy devices (such as a mobile phone) to be part of a Bluetooth mesh network. Proxy nodes expose a GATT interface which Bluetooth LE devices may use to interact with a mesh network. A Proxy Node can receive messages over one bearer (advertising or GATT) and retransmit them over the other (advertising or GATT). The fundamental purpose of the Proxy Node is to perform bearer conversion. It can convert from the advertising bearer to the GATT bearer and vice versa. Therefore, a device which does not support the advertising bearer may instead send and receive various types of Bluetooth mesh messages over a GATT connection. For example, the function is useful when the user wants to use a traditional smart phone to control a smart lighting network. The interaction is realized through GATT data transmission of the node and the device.
5. Bluetooth MESH アーキテクチャ
Bluetooth メッシュ ネットワークは、「フラッディング」テクノロジーを使用してネットワーク内にメッセージを送信します (これはウイルスが拡散する方法と似ています)。各データ パケットは、メッセージがターゲット ノードに到達するまで、ネットワーク内の他のノードに転送されます。メッセージ ブロードキャストは、単一ノード、ノードのグループ、およびすべてのノードに対して行うことができます。たとえば、単一の部屋のすべての照明をグループ アドレスとして定義できます。Bluetooth メッシュ仕様では、「All-Proxies」、「All-Friends」、「All-Relays」、および「All-nodes」の 4 つの固定グループ アドレスが定義されています。(LPN には低消費電力を維持する必要があるため、メッセージを転送する機能はありません。)
フラッディング メッシュ アーキテクチャとグループ アドレスの選択により、スマート ホーム アプリケーションの Bluetooth メッシュ ネットワークのサポートが強化されます。たとえば、MESH ネットワーク内のゲートウェイ デバイスが「ON」コマンドを受信すると、そのコマンドは MESH ネットワークを通じてネットワーク全体に迅速にブロードキャストできます。ネットワーク内の各ノード デバイスはコマンドを受信し、それに応じてアクションを実行し、ターゲット グループ内のライトを即座に点灯させることができます。
スター型ネットワークと比較すると、MESH ネットワークノードの平均受信データの最小待ち時間はスター型ネットワークよりも大幅に短くなります。中央装置はスター型ネットワーク内の接続された各電球に個別のコマンドを送信する必要があるためです。そして、CPU は一定の間隔ですべてのサブデバイスにコマンドを送信する必要があります。
Bluetooth MESH と従来の Bluetooth にはいくつかの違いがあります。すべてのメッシュ データは 3 つの広告チャネル 37、38、および 39 でのみ送信されます。これには長所と短所があります。利点は高効率とシンプルな伝送方法です。また、ネットワーク帯域幅が減少し、輻輳のリスクが高まるという欠点があります。
MESH ネットワークが輻輳を処理するには 2 つの方法があります。1 つ目はTTL (Time To Live)で、特定のパケットを転送できる回数を定義します (通常は 3 ステップ)。2 つ目はネットワーク キャッシュです。デバイスは、転送されたデータ パケットをキャプチャした後に 1 回だけブロードキャストします。デバイスは、次回他のデバイスによってブロードキャストされた同じ情報パケットを受信した場合、それ以上転送しません。
開発者は、オプションのグループ配信ルートを使用してリレー機能を保持することもできます。設定後、ノードはデータパケットを受信できますが、送信できなくなります。したがって、ノードの柔軟性が悪くなります。
6.BLEメッシュモデル
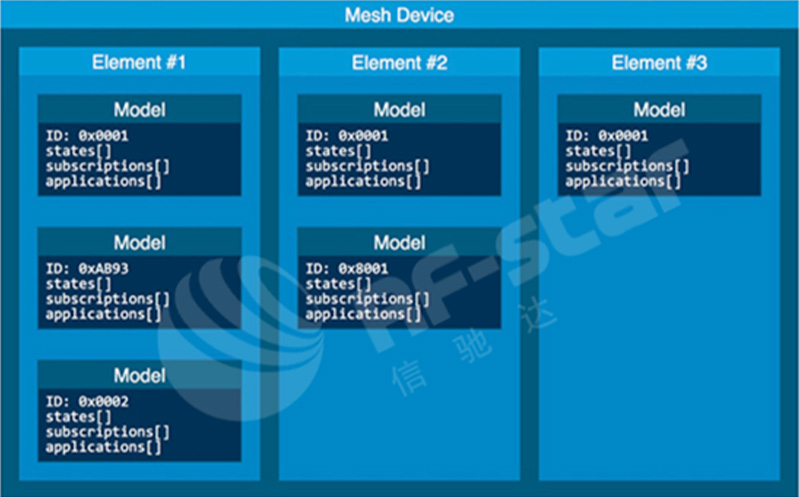
MESH モデルの概念は Bluetooth プロファイルの概念に似ています。モデルは、1 つ以上のサービスを含めることができる公開情報構造を指定します (モデルの概念は、端末デバイスを定義するために使用されます)。
モデルにはノードの特定の動作とサービスが含まれており、一連のステータスとそのステータスに作用するメッセージを定義します。標準モデルは、デバイス構成、センサー読み取り値、照明制御などの一般的なアプリケーションで動作します。また、開発者はカスタム モデルを作成することもできます。
ノード内のモデルは要素ごとに配置されます。各要素は、一意のアドレスを持つメッシュ内の仮想エンティティとして機能し、各受信メッセージは要素内のモデルによって処理されます。
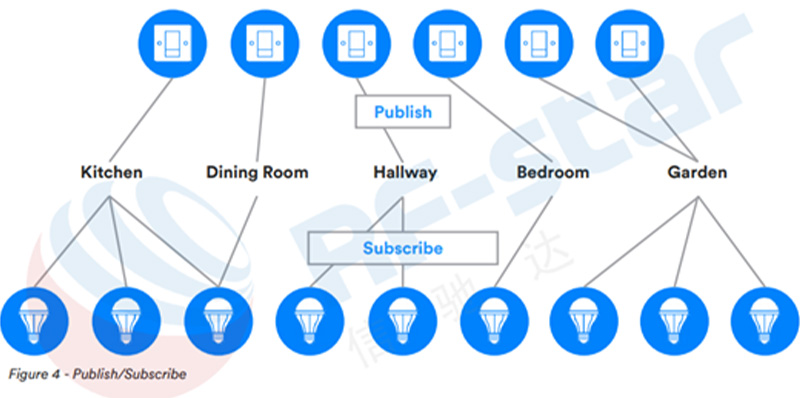
さまざまなモデルは、「パブリッシュとサブスクライブ」を通じて相互に対話します。パブリッシング ノードがメッセージを送信し、サブスクライブするように構成されたノードがメッセージを受信した後にそのメッセージを処理します。
次の図では、ノード「Switch 1」がグループ アドレス Kitchen に公開していることがわかります。ノード Light 1、Light 2、および Light 3 はそれぞれキッチン アドレスをサブスクライブするため、このアドレスに発行されたメッセージを受信して処理します。つまり、ライト 1、ライト 2、およびライト 3 は、スイッチ 1 を使用してオンまたはオフに切り替えることができます。
スイッチ 2 は、グループ アドレス Dining Room にパブリッシュします。ライト 3 だけがこのアドレスにサブスクライブしているため、スイッチ 2 によって制御される唯一のライトです。この例は、ノードが複数の異なるアドレスにアドレス指定されたメッセージをサブスクライブできるという事実も示していることに注意してください。これは強力かつ柔軟です。
同様に、スイッチ 5 とスイッチ 6 の両方のノードが同じガーデン アドレスにパブリッシュしていることに注目してください。
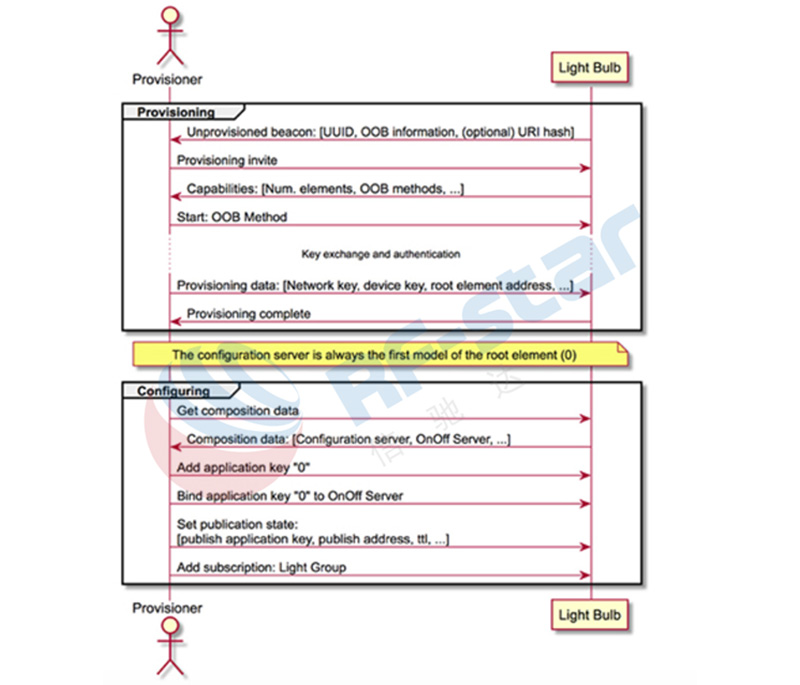
7. Bluetooth メッシュ構成ネットワーク
8. Bluetooth MESH アプリケーション
SIG 認証製品の予備統計に基づくと、BLE MESH のアプリケーションは主にスマート ホームと照明制御アプリケーションに集中しており、照明制御が 60%、スマート ホームが 30%、残り 10% を占めていることがわかります。メーカーのオリジナルチップ認証とニッチ市場アプリケーションに属します。BLE MESH は間違いなくZigBeeの最大の競合相手です。